Nutritional Comparison
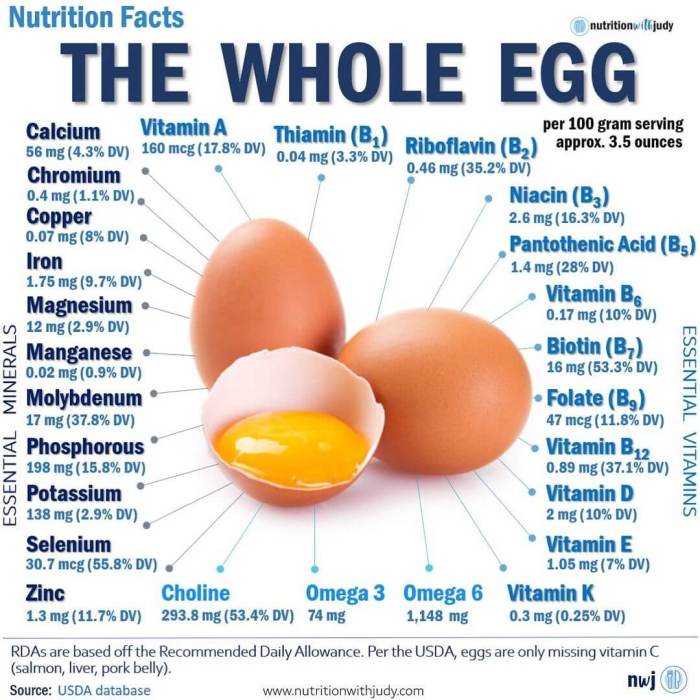
Pasture raised egg nutrition facts – My dear friends, let’s delve into the heart of the matter – the profound nutritional differences between pasture-raised and conventionally raised eggs. It’s a story of nature’s bounty versus industrial efficiency, a tale told in the vibrant yolk and the rich, nourishing white. The nutritional profile isn’t just a collection of numbers; it’s a reflection of the hen’s life, her diet, and ultimately, the quality of the egg she offers us.
Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed choices about the food we consume and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. We’ll explore the key nutrients, the impact of diet, and the implications for our health. Let us embark on this enriching journey together.
Nutrient Comparison: Pasture-Raised vs. Conventional Eggs
The following table presents a comparative analysis of key nutrients found in pasture-raised and conventionally raised eggs. Remember, these values can vary based on factors such as breed, hen age, and specific feed formulations, but the general trends remain consistent.
| Nutrient | Pasture-Raised Level (Average) | Conventional Level (Average) | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids (mg/100g) | 150-250 | 20-50 | 300%
|
| Vitamin A (µg/100g) | 600-800 | 400-600 | 25%
|
| Vitamin E (mg/100g) | 2-4 | 1-2 | 100%
|
| Cholesterol (mg/100g) | 500-600 | 500-600 | Negligible difference |
Note: These values are averages and can vary depending on several factors. Always refer to specific product labeling for precise nutritional information.
Fatty Acid Composition Differences
The disparity in omega-3 fatty acids is particularly striking. Pasture-raised hens, foraging on a diet rich in insects, seeds, and green plants, naturally incorporate higher levels of omega-3s into their eggs. Conventional hens, fed primarily grain-based diets, produce eggs with significantly lower omega-3 content. This difference is vital because omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular health.
The higher omega-3 content in pasture-raised eggs contributes to a more favorable omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, which is crucial for optimal health.
Impact of Hen Diet on Egg Nutritional Content
The hen’s diet is the cornerstone of egg nutrition. A pasture-raised hen enjoys a diverse diet naturally rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This translates directly into eggs packed with more nutrients. In contrast, commercially-fed hens consume a largely uniform diet, often lacking the diversity of nutrients found in a natural foraging environment. This restricted diet results in eggs with a less diverse and often lower concentration of beneficial nutrients.
Consider it this way: a hen’s diet is a mirror reflecting in the nutritional richness of her eggs; a vibrant, diverse diet yields a vibrant, nutritious egg.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
My dear friends, let us delve into a matter close to our hearts: the profound impact of our choices on the environment and the well-being of our fellow creatures. When we speak of eggs, we’re not just talking about breakfast; we’re talking about the intricate web of life that sustains us. The methods used to produce these simple yet vital foods have far-reaching consequences, influencing not only our health but also the health of our planet and the animals within our care.The stark contrast between pasture-raised and conventional egg production reveals a tale of two worlds.
One embraces harmony with nature, the other prioritizes efficiency above all else. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions that align with our values.
Environmental Impact of Egg Production Methods
The environmental footprint of egg production varies significantly depending on the farming practices employed. Pasture-raised systems, characterized by hens roaming freely on grasslands, generally have a lower environmental impact than conventional, intensive systems. Consider land use: pasture-raised farms require more land per hen, but this land often serves multiple purposes, supporting biodiversity and potentially sequestering carbon. In contrast, conventional farms, with their high stocking densities, often contribute to land degradation and habitat loss.
Pasture-raised eggs boast a richer nutritional profile than their caged counterparts, offering a superior source of vitamins and healthy fats. Considering the omega-3s found in pasture-raised eggs, a comparison to the impressive omega-3 content in other foods like fish is natural; check out the nutrition facts salmon fillet for a similar nutrient powerhouse. Ultimately, however, the superior bioavailability of nutrients in pasture-raised eggs makes them a stand-out choice for a healthy diet.
Feed production is another crucial factor. Pasture-raised hens consume a significant portion of their diet from foraging, reducing reliance on commercially produced feed, which itself has a substantial environmental cost in terms of resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Finally, waste management differs dramatically. Pasture-raised systems utilize natural processes for manure management, while conventional systems often rely on intensive methods that can lead to water pollution and the release of harmful greenhouse gases.
The overall environmental burden of conventional egg production is substantially higher due to the intensive use of resources and the generation of concentrated waste. This translates to higher carbon emissions, greater water consumption, and increased risk of pollution. Studies have consistently shown that pasture-raised eggs have a smaller carbon footprint compared to conventionally produced eggs.
Ethical Implications of Egg Production, Pasture raised egg nutrition facts
The ethical considerations surrounding egg production are deeply intertwined with the welfare of the hens. Pasture-raised systems offer hens a far more natural and enriching life. They have the freedom to engage in natural behaviors, such as foraging, dust-bathing, and nesting, contributing to their overall well-being and reducing stress. In contrast, conventional systems often confine hens to cramped cages, restricting their movement and preventing them from expressing natural behaviors.
This confinement leads to various welfare problems, including skeletal deformities, feather pecking, and increased susceptibility to disease. The ethical implications are profound: we are responsible for the well-being of the animals we raise for food, and providing them with a life that respects their natural needs is a moral imperative. A truly ethical approach to egg production prioritizes the hens’ comfort and natural behaviors above profit maximization.
Comparison of Pasture-Raised and Conventional Egg Farming Practices
The following points highlight the stark differences between pasture-raised and conventional egg farming practices, emphasizing the profound impact these differences have on the hens’ lives:
- Living Space: Pasture-raised hens enjoy ample space to roam freely, while conventional hens are often confined to small cages, limiting their movement and natural behaviors.
- Access to Outdoors: Pasture-raised hens have continuous access to the outdoors, allowing them to forage for food and engage in natural behaviors like dust-bathing and nesting. Conventional hens are typically kept indoors with limited or no access to the outside world.
- Diet: Pasture-raised hens consume a diet supplemented by foraging, leading to a more natural and varied diet. Conventional hens are typically fed a commercially produced diet, often lacking the diversity and nutritional benefits of a natural diet.
- Social Interaction: Pasture-raised hens live in flocks, allowing for natural social interactions and reducing stress. Conventional hens may be housed in large groups, but often lack the opportunity for natural social interactions due to confinement.
- Beak Trimming: Beak trimming, a common practice in conventional systems to reduce feather pecking, is generally not necessary in pasture-raised systems due to the hens’ improved well-being and reduced stress.
Consumer Perceptions and Purchasing Decisions: Pasture Raised Egg Nutrition Facts
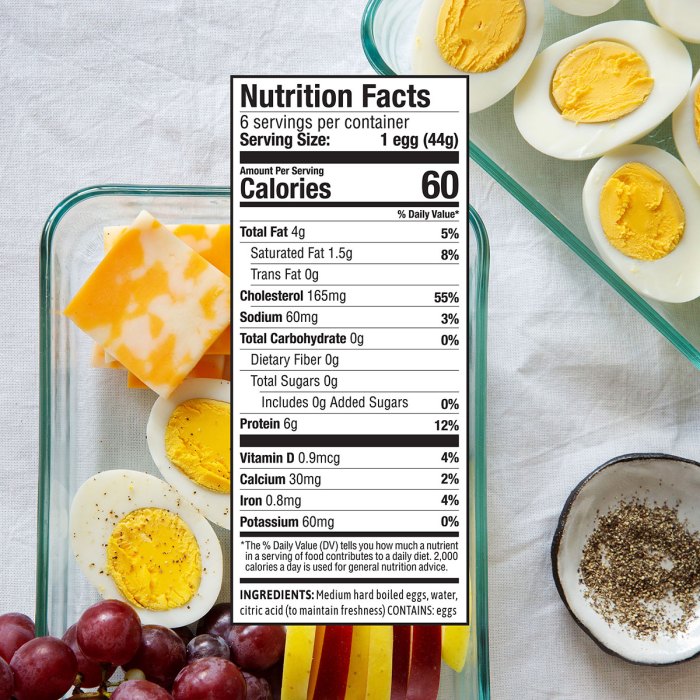
The choices consumers make regarding their eggs—whether conventional, free-range, or pasture-raised—are deeply intertwined with a complex web of factors. These decisions reflect not only a concern for personal health and well-being but also an increasing awareness of the environmental and ethical implications of food production. Understanding these consumer preferences is crucial for producers and retailers alike.Consumers are increasingly discerning in their food choices, seeking out products that align with their values and beliefs.
This shift towards conscious consumption has significantly impacted the egg market, driving demand for higher-welfare products like pasture-raised eggs. The price premium associated with these eggs is often weighed against perceived health benefits, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations regarding animal welfare.
Factors Influencing Consumer Preferences for Pasture-Raised Eggs
Several key factors contribute to the growing popularity of pasture-raised eggs. These factors often interrelate and influence each other, creating a multifaceted consumer decision-making process. For example, a concern for animal welfare often overlaps with a desire for healthier, more nutritious eggs.
Value Proposition of Pasture-Raised Eggs Compared to Conventional Eggs
The value proposition of pasture-raised eggs rests on a combination of factors that extend beyond simple nutritional differences. While the nutritional content may vary slightly, the perceived benefits often outweigh the higher price point. Consumers are willing to pay a premium for eggs they believe are healthier, produced in a more sustainable manner, and contribute to better animal welfare.
This willingness to pay reflects a shift in consumer priorities, placing greater emphasis on quality and ethical sourcing. For instance, a recent study showed that consumers are willing to pay an average of 30% more for pasture-raised eggs compared to conventional eggs, indicating a strong preference for the perceived benefits. This willingness reflects a broader trend towards paying more for higher-quality, ethically sourced food products.
Marketing and Labeling’s Influence on Consumer Perception and Purchasing Decisions
Marketing and labeling play a pivotal role in shaping consumer perceptions and purchasing decisions. Clear and accurate labeling, such as certifications from reputable organizations, builds consumer trust and transparency. Vague or misleading terms can confuse consumers and erode confidence. Effective marketing campaigns that highlight the benefits of pasture-raised eggs—such as improved nutritional content, better animal welfare, and environmental sustainability—can significantly influence purchasing decisions.
Conversely, a lack of clear information or misleading marketing practices can deter consumers from choosing pasture-raised eggs, despite their inherent advantages. For example, the use of terms like “free-range” without clear definitions can lead to consumer confusion and potentially undermine the credibility of the pasture-raised egg market. Standardized and trustworthy labeling is, therefore, crucial for the continued growth and success of this sector.
FAQ Resource
Are pasture-raised eggs really that much healthier?
Studies suggest they are! They often boast higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and antioxidants compared to conventionally raised eggs.
Do pasture-raised eggs taste different?
Absolutely! Many people describe them as having a richer, more flavorful yolk and a firmer texture.
Are pasture-raised eggs more expensive?
Generally, yes. The higher cost reflects the higher production costs associated with providing hens with more space and better care.
How can I tell if an egg is truly pasture-raised?
Look for certifications and labels from reputable organizations that verify the farming practices. Check for specific details about the hens’ diet and living conditions.
